Nutritious mushrooms are a key source of food and income in various countries around the world. The main producers are five types: button mushroom (Agaricus bisporus) and Brazilian agaricus (A. subrufrescens) together account for 30%, oyster mushrooms (Pleurotus sp.) - 27%, shiitake (Lentinula edodes) - 17%, wood ear (Auricularia sp.) - 6%, and enoki (Flammulina sp.) - 5%.
Various agricultural wastes are used for cultivation, such as corn husks, straw, sawdust, sugar cane bagasse, cottonseed hulls, and coffee residues.
For every kilogram of fresh mushrooms produced, about 5–6 kg of mushroom waste is generated, creating waste management issues.
Reusing mushroom waste on farms can reduce waste accumulation, protect against pollution, and preserve nutrients by processing organic waste into fertilizers or biopesticides.
Phytoparasitic nematodes are a major biotic factor hindering agriculture, causing annual crop losses of 12.3–12.6% globally and economic damages amounting to billions of dollars.
The most harmful nematodes include root-knot nematodes Meloidogyne spp., cyst-forming nematodes (Heterodera and Globodera spp.), root lesion nematodes Pratylenchus spp., and burrowing nematode (Radopholus similis).
Nematodes pose a threat to the banana industry and are a problem in mixed populations, such as Meloidogyne spp., Pratylenchus spp., Helicotylenchus multicinctus, and R. similis.
R. similis attacks various tropical plants, including bananas, causing significant root damage that impairs water and nutrient uptake, making plants more vulnerable.
The use of chemical pesticides is risky for the environment and human health. Therefore, using mushroom waste in organic production can be an alternative for nematode management.
A study on the potential of oyster mushrooms to combat nematodes, published in the journal Agronomy 2025, highlights successes in reducing the damage from R. similis on banana trees.
The evaluation regimen included two experiments under banana cultivation conditions from May 2023 to June 2024.
The results showed that using spent mushroom substrate improves banana growth, reduces root damage, and R. similis population, which could be a promising solution in the future.

 Trading platform
Trading platform 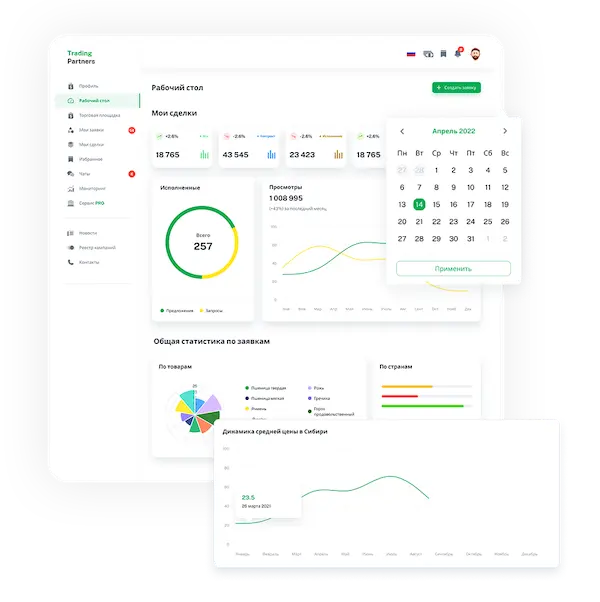
 Monitoring
Monitoring  Express applications
Express applications 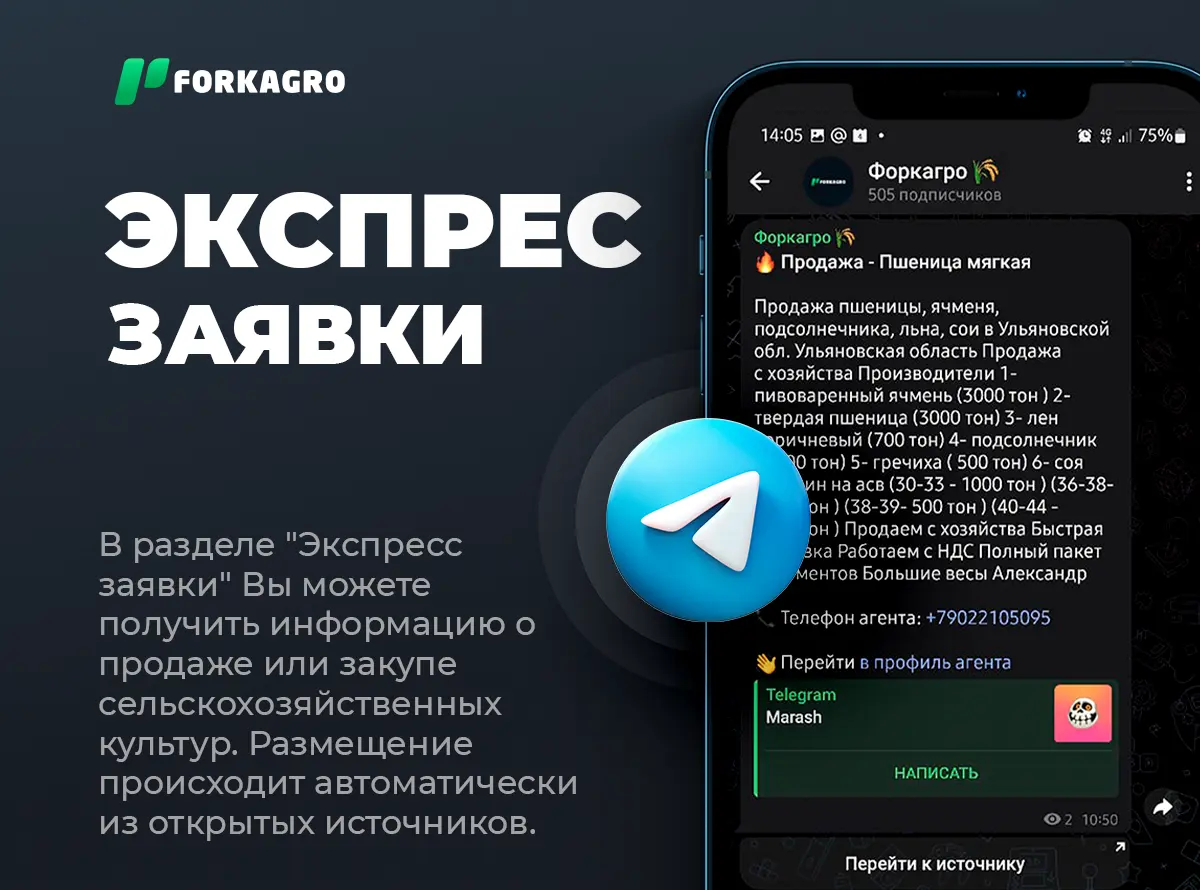
 Fork Work
Fork Work 
 Service
Service  News
News  Directory
Directory