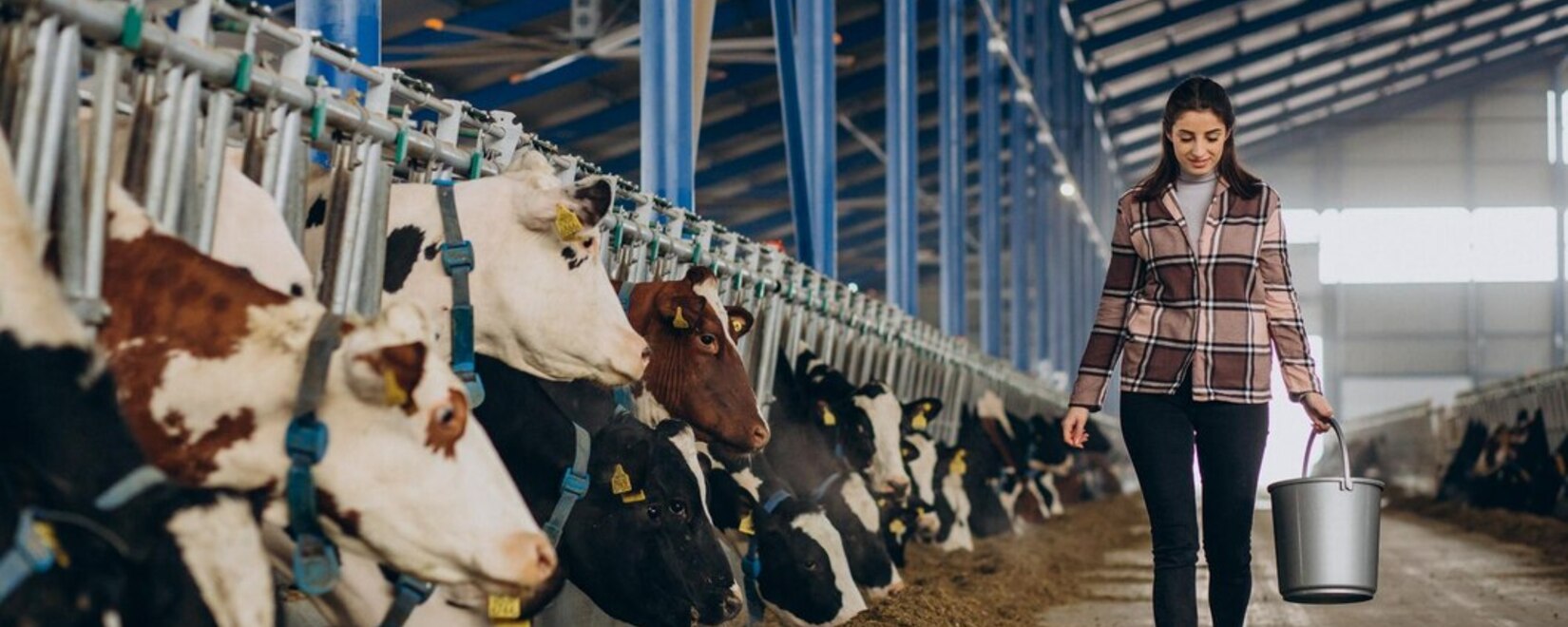
At an Indian scientific institute, the cause of the increasingly frequent outbreaks of nodular dermatitis (infectious nodular dermatitis, IND) in cattle has been revealed.
As part of the research, over 1,800 genetic variants of the pathogen causing this disease, which was found exclusively in the country, were collected. Scientists concluded that the high number of cases is due to the genetic diversity of the pathogen. Together with local veterinary organizations, a check for the presence of the disease has been conducted throughout the country since 2022, resulting in over two million animals becoming infected and over a million cows dying. However, details on the direction of livestock productivity are not provided. Samples of nodules on the skin (one of the main symptoms of the disease), as well as blood and swabs from the noses of infected livestock from various regions of India, were taken during the study. Whole-genome sequencing (determination of amino acid and nucleotide sequences) of the virus was carried out. As a result of the analysis, two main strains were identified. One of them had slight genetic diversity and was similar to the Ranchi and Heyderabad strains from 2019 and 2020, previously detected during previous outbreaks. The second strain had 1,819 different variants in 22 genome sequences. This strain was similar to the IND strains detected during the outbreak in Russia in 2015.
Such a large number of pathogen variants came as a surprise to the scientists. However, they found an explanation for this fact. It turned out that variations were mainly observed in genome regions responsible for binding to target cells, evading the immune response, and cell replication. Researchers also found that the most severe cases of the disease were registered in animals from areas with the highest number of genetic infection variants. This led to the assumption that genetic variations contribute to increased virulence and pathogenicity of the pathogen. Researchers believe that the results obtained will help improve the diagnosis of this disease, develop vaccines, and establish a prevention plan.
Nodular dermatitis (infectious nodular dermatitis) is one of the most dangerous viral diseases in cattle. The main symptoms include fever and lesions of many organs and areas (including eyes, skin, lymphatic system, and respiratory and digestive organs). Asymptomatic form of the disease is also possible, which can be even more dangerous and lead to the unexpected death of the animal. Animals that have had this disease also experience exhaustion, decreased milk yield, skin damage, and reproductive dysfunction. It is important to note that this disease is not zoonotic and does not pose a threat to humans.

 Trading platform
Trading platform 
 Monitoring
Monitoring  Express applications
Express applications 
 Fork Work
Fork Work 
 Service
Service  News
News  Directory
Directory 
