Sugar, also known as sucrose, is an organic compound extracted from various plant sources for commercial use. The primary plants used in sugar production are sugarcane and sugar beet.
Over a thousand years ago, sugarcane was used to obtain sugar, while sugar beet became a popular source of sugar only from the mid-19th century. In Europe, a major portion of sugar is produced from sugar beet, while in some African countries, the USA, and China, both sources are used.
Sugarcane originates from New Guinea, and there are records of its cultivation in that region as far back as 8000 BC. The oldest written mention of sugar refining dates back to 100-650 AD and comes from India.
The technology of sugar production then spread to the Arab world, where sugar was used for culinary purposes and to create edible decorations, such as marzipan.
Europe was introduced to sugar thanks to the Arabs, but until the 1300s, Europeans did not know how to produce it, so sugar was considered a delicacy available only to the wealthiest people.
Starting from the early 15th century, European colonizers began growing sugarcane in their tropical colonies. This practice continued until 1747 when the Prussian chemist Andreas Marggraf discovered that sucrose could also be extracted from sugar beet.
Sugarcane is a tropical plant that grows up to 4 meters in height and thrives in areas with abundant rainfall. It reproduces mainly through vegetative means.
The stem of the sugarcane, consisting mainly of water, fiber, and soluble sugars, is the primary source of sugar in the plant.
After harvesting, the sugarcane is transported to processing facilities where it is crushed to extract the juice. This juice is boiled, allowing the water to evaporate and leaving behind sugar crystals. These crystals are purified from impurities, then dried and packaged for sale.
On the other hand, sugar beet is a plant that grows in a temperate climate and has a conical white root containing sugar produced through photosynthesis by the leaves. The root consists mainly of water, soluble sugars, and pulp.
When the beets are harvested, they are transported to a factory where they are cleaned and sliced into small pieces. These pieces are soaked in water, allowing the sugar to dissolve and form a sugar solution. Then impurities are removed, and the process of purifying and drying the sugar is very similar to the one used for sugarcane sugar production.

 Trading platform
Trading platform 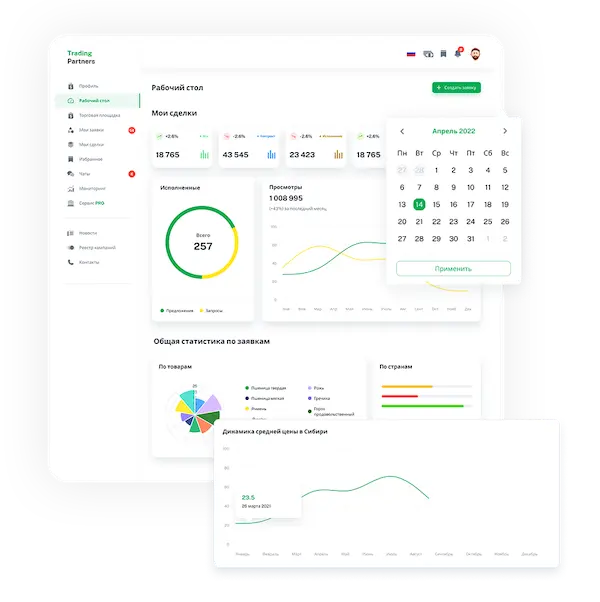
 Monitoring
Monitoring  Express applications
Express applications 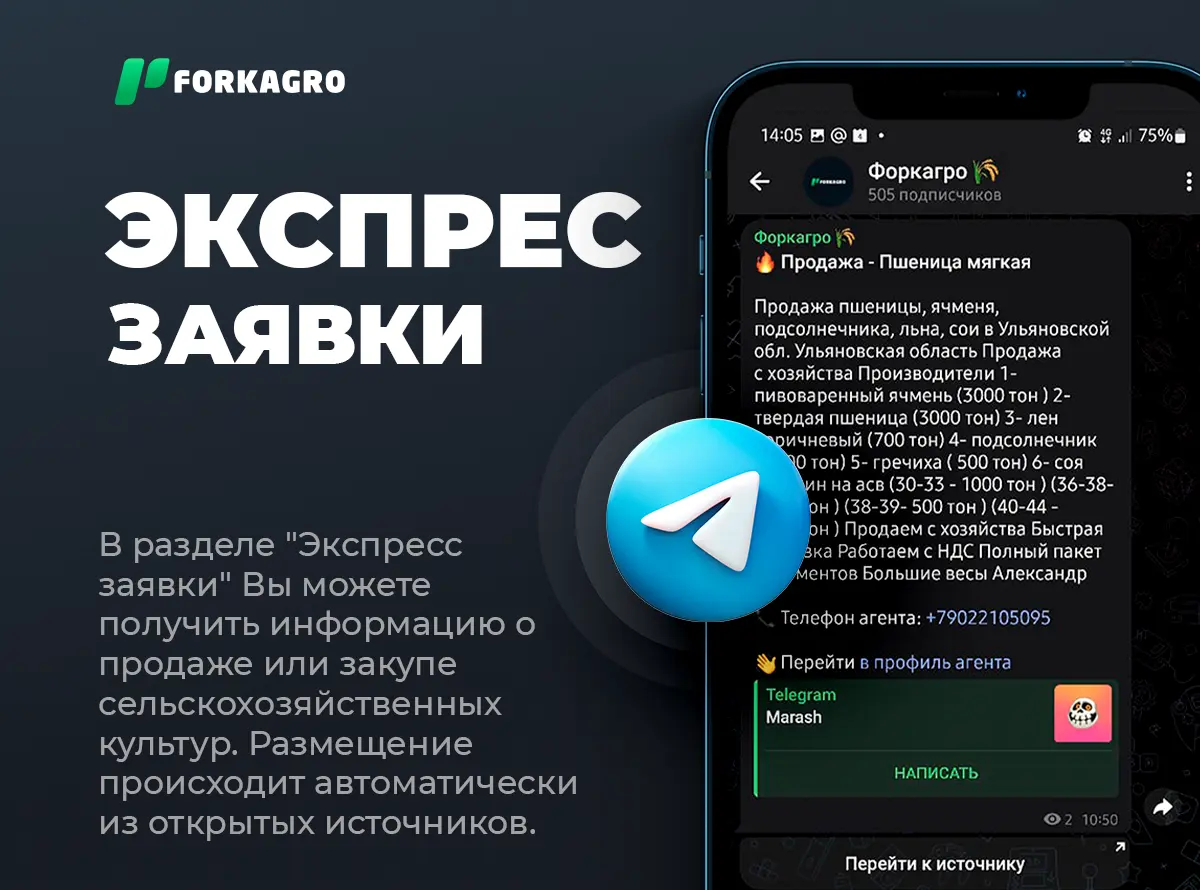
 Fork Work
Fork Work 
 Service
Service  News
News  Directory
Directory 
